6.0 Unit 6 Overview: Industrialization and Its Effects
4 min read•january 28, 2023
Eric Beckman
Jillian Holbrook
Eric Beckman
Jillian Holbrook
AP European History 🇪🇺
335 resourcesSee Units
Industrialization
Using machines, factories, and fossil fuels defined the Industrial Revolution. 🏭 Technological advancements emerged, such as the steam engine and the power loom, which led to the mechanization of manufacturing. Ultimately, this sparked a shift from agrarian and handicraft economies to industrial ones.
Along with urbanization and capitalist economic structures, these factors dramatically increased production and altered society.
The First Industrial Revolution
The first industrial revolution began in Britain. Enormous profits from British colonial trade, especially the slave trade and slave-produced sugar, provided capital (money to invest) which was essential for purchasing machines and building factories. 🚜
British banks and other financial institutions made capital available to investors. British capitalists, workers, and engineers mechanized the production of textiles (cloth), increased iron and steel production, and built railroads. 🛤
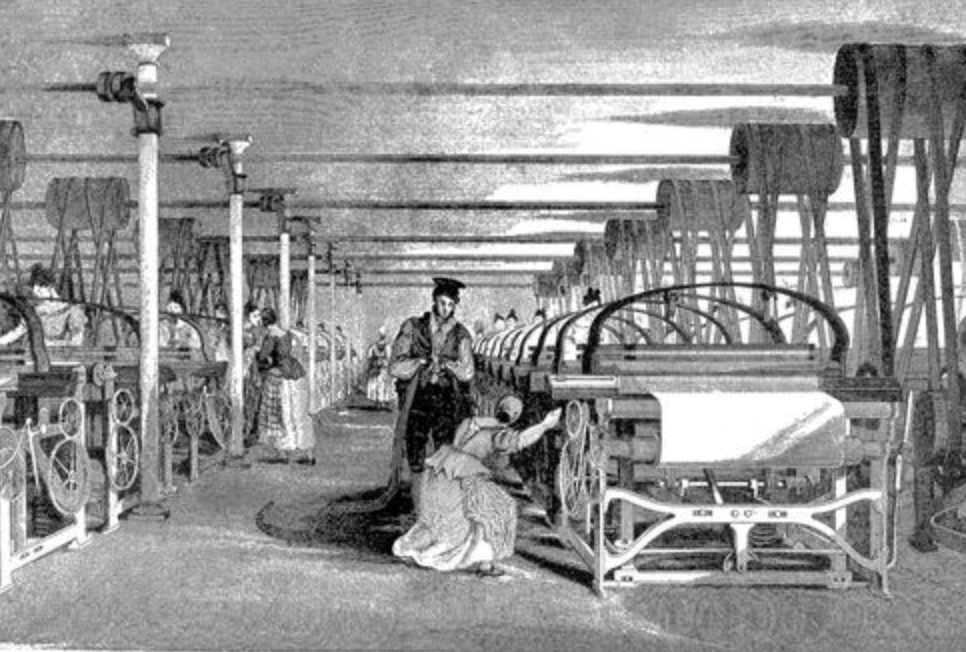
Textile production in Britain, 1835
Soon after, industrial capitalism began in other areas of Europe, especially parts of France and Belgium. Governments there were frequently involved with direct investment in railroads and factories.
However, areas of Europe without key resources for industry or with more primitive agriculture (e.g., less productive, the persistence of serfdom, socially powerful landed elites) did not industrialize and faced agrarian crises such as the Irish Potato Famine.
(*Agrarian: having to do with agriculture or farming)
The Second Industrial Revolution, c. 1870-1914
Industrialization was (and is!) an ongoing process. New transportation networks, such as railroads and steamship routes, in industrial areas like Britain and the Rhineland made large-scale factory production possible. These networks and inventions facilitated new industries and greater steel production, which supported massive urbanization and industry spread to more areas.
This growth of industrial capitalism produced rapid ups and downs in economic life. Prussia was home to a lot of this economic growth and became a more powerful state. 📈

Steam-powered ocean liner, 1908
Society in the Era of Industrialization
Industrialization deeply affected everyday life, and these effects varied based on the degree of industrialization.
Consumerism
In general, people bought more goods and, eventually, working people had more leisure time. The ever-increasing pursuit of material goods, services, and recreation defines consumerism. Increased production and more available transportation from the Second Industrial Revolution facilitated the rise of consumerism.

French department store, a palace for consumerism
Social Structures
Commercialization and industrialization (i.e., new equipment, better transportation) of farming increased population size, especially in cities. Millions of people moved from the country to cities as part of this process, which upset traditional social orders in the country and the city.
New divisions of labor from industrialization produced larger classes: the proletariat (people doing physical work for wages) and the bourgeoisie (people investing in or managing capitalist production). The bourgeoisie was increasingly powerful in industrial areas, but in less industrialized countries like Russia, traditional agricultural elites remained dominant. 🇷🇺
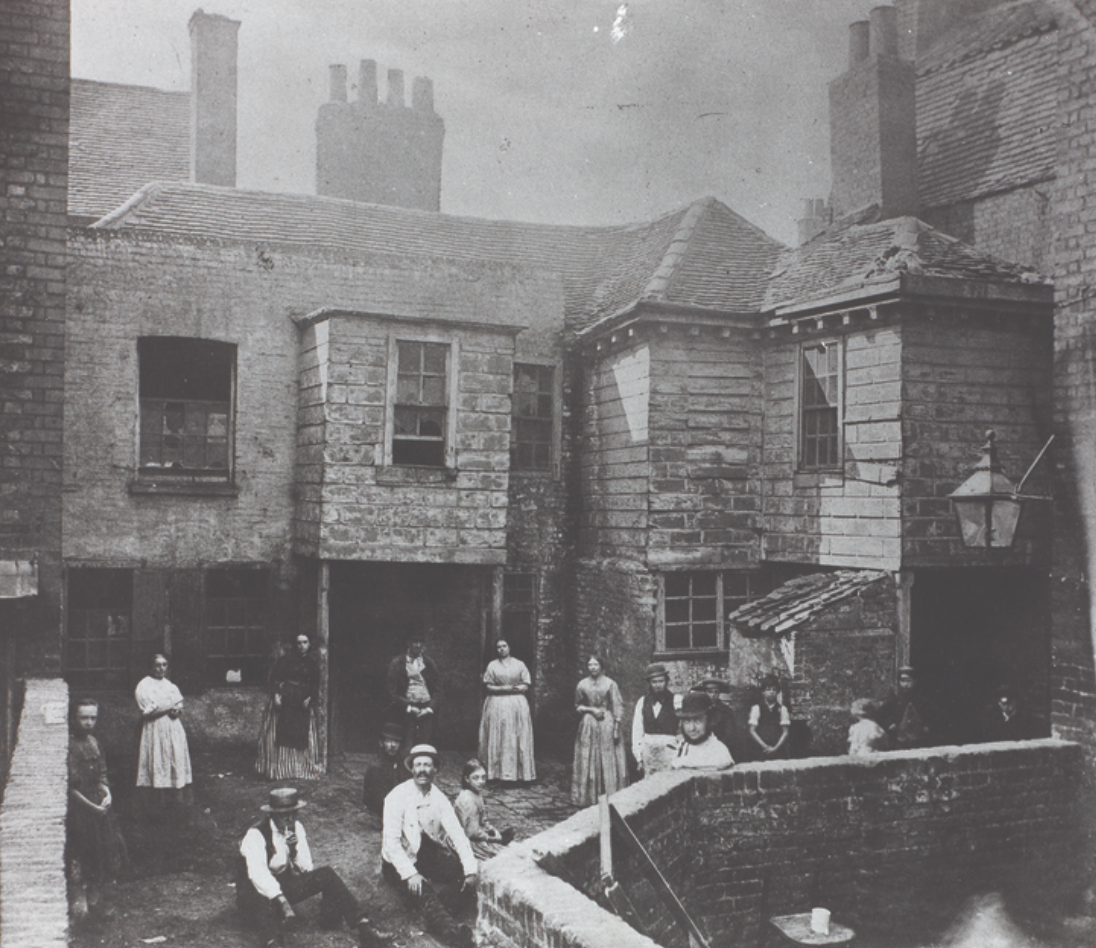

Image from Wikipedia Working-class housing, London, 1860s
Social class greatly affected people’s experiences in industrial society. Working-class (i.e., proletarian) neighborhoods in growing cities were often overcrowded and unsanitary; working conditions were terrible. Unions, mutual aid societies, and government reforms aimed to improve working and living conditions. Along with increasing production (lowering prices), they did so for many.
Middle-class (i.e., bourgeois) families developed a social identity through associations and family culture stressing fewer children and distinct gender roles. Over time, working-class people adopted these ideals.
Revolutions and Responses
Social change from industrialization combined with political revolutions to influence Europe, c. 1815 - c. 1914.
📄 Study AP European History, Unit 5.7: The Congress of Vienna
Concert of Europe
The Concert of Europe is also known as the Congress system, after the Congress of Vienna, 1814-1815. Both aimed to protect traditional elites—churches, monarchs, and nobles–after disrupting the French Revolution and Napoleon’s conquests. This effort contributed to the emerging ideology of conservatism, which worked against change and supported traditional authorities. 🏛
Revolutions
Conservative leaders were unable to stop revolutions, although they did defeat most attempts to transform society. Political and economic grievances (complaints) combined to make 1848 a year of revolutions across Europe. Later, reforms changed Russia, but not enough to prevent revolutionary groups, which instigated the Revolution of 1905. Few revolutions succeeded completely, but they did contribute to new ideologies and reforms. 💬
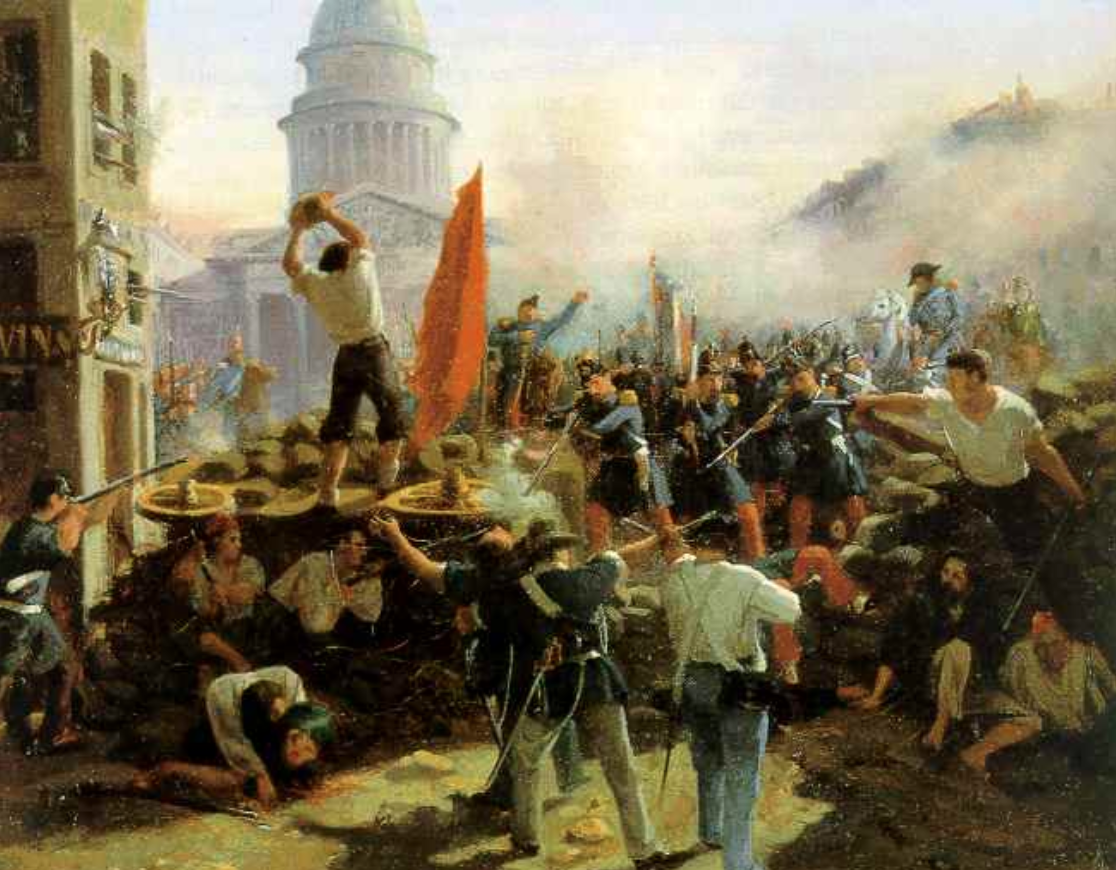

Revolution of 1848, Paris
New Ideologies
Political and economic revolutions gave rise to several new ideologies, aka “isms:” systems of ideas and ideals that structure how people view the world. Liberalism supported the moderate French Revolution ideals: individual rights, free markets, and popular sovereignty. In many European countries, most men could vote by 1900. Political parties, thus, developed mass constituencies as they competed for votes. Feminist organizations worked to secure voting and other rights for women. 🗳

Britain, 1908
Socialists, on the other hand, responded to industrial capitalism by advocating for a more equal distribution of resources. The scientific socialism theorized by Karl Marx criticized capitalism and predicted a revolution. Anarchists wanted to smash governmental authority in order to increase both political freedom and economic equality.
Reforms
Instead of revolution, many people responded to industrial problems by reforming society through social organizations and political parties. Governments responded to these efforts by improving infrastructure (e.g., water, sewage, and parks), thereby increasing the quality of urban life. Several governments in industrializing countries also passed laws limiting working hours for children and women. Finally, public education systems encouraged nationalism and thus attempted to discourage revolution while hoping that educated citizens would produce stronger economies.
Browse Study Guides By Unit
🎨Unit 1 – Renaissance & Exploration
⛪️Unit 2 – Reformation
👑Unit 3 – Absolutism & Constitutionalism
🤔Unit 4 – Scientific, Philosophical, & Political Developments
🥖Unit 5 – Conflict, Crisis, & Reaction in the Late 18th Century
🚂Unit 6 – Industrialization & Its Effects
✊Unit 7 – 19th Century Perspectives & Political Developments
💣Unit 8 – 20th Century Global Conflicts
🥶Unit 9 – Cold War & Contemporary Europe
🚀Thematic Guides
📝Long Essay Questions (LEQ)
📆Big Reviews: Finals & Exam Prep

© 2023 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.